
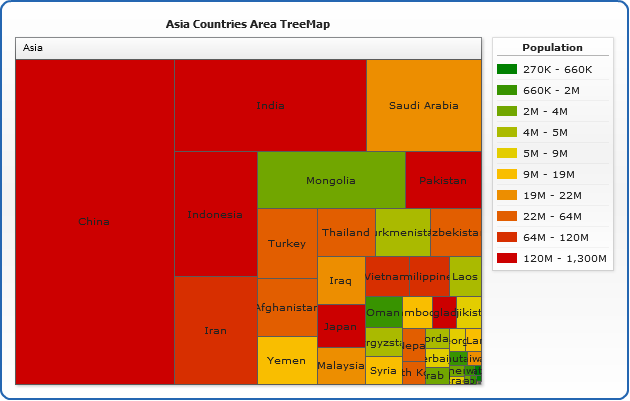
They can be used when there are a number of data items present and you want see the general relationships. Bubble charts show correlations among three types of values. In a Bubble Chart the data is represented by the location and size of round data markers (bubbles). A node is assigned a color based on the range into which the value falls. All the nodes that have a color data value greater than the lower cutoff and lower than or equal to the upper cutoff are shaded with the associated color.ĭefines the color associated with each group. If you add a group (by changing the value in Number of groups), the new group will initially be assigned a default name, regardless of any changes you may have made.ĭefines the cut-off value for the range associated with the group. You can change these names as appropriate. The default names are Group 1 and Group 2. This option is more relevant when color data aggregates as total, min, max, and so on. You may not need the On drill option when the data that drives color is aggregated as average, mean, median, or percent. The new cutoffs are based on the new color data and proportioned using the parent-level cutoffs. Select this option so that after drilling down, you want the range cutoff values to be proportional. In this case, the Value check box becomes de-selected. You can override these auto-calculated values by entering a range cutoff value yourself. Select this option if you want the range of cutoff values to be auto-calculated based on Number of groups and chart data. Table 12-8 Grouped Subtype Options Optionĭefines the number of discrete groups that the nodes are grouped into. When you select the grouped subtype, you must manage the options for Number of groups, Auto Fill, Labels, Range cut-off values, and Color. The default values are derived from PivotTableStyles.properties. These values are auto-calculated if you select the Auto Fill check box.Īssociates a specific color with the minimum value and a specific color with the maximum value. Nodes with values in between are reflected by color shades according to their specific values. Treemap chart nodes that have values less than or equal to the minimum are shaded with the color associated with the minimum value, and nodes with values greater than or equal to the maximum are shaded with that associated color. This option is more relevant when color data aggregates as total, min, max, and so on.ĭefine the starting and ending values for the color transition. Select this option so that after drilling down, the minimum and maximum values are re-calculated based on the new highest and lowest values instead of on the existing parent-level values. You can override these auto-calculated values by entering a number for either value yourself. The minimum value is set to the lowest chart data value, and the maximum value is set to the highest chart data value. Select this option if you want the minimum and maximum values to be auto-calculated based on the chart data. These two options are both selected by default.

Select this check box if you want Values or On drill to be auto-calculated. Table 12-7 Continuous Subtype Options Option
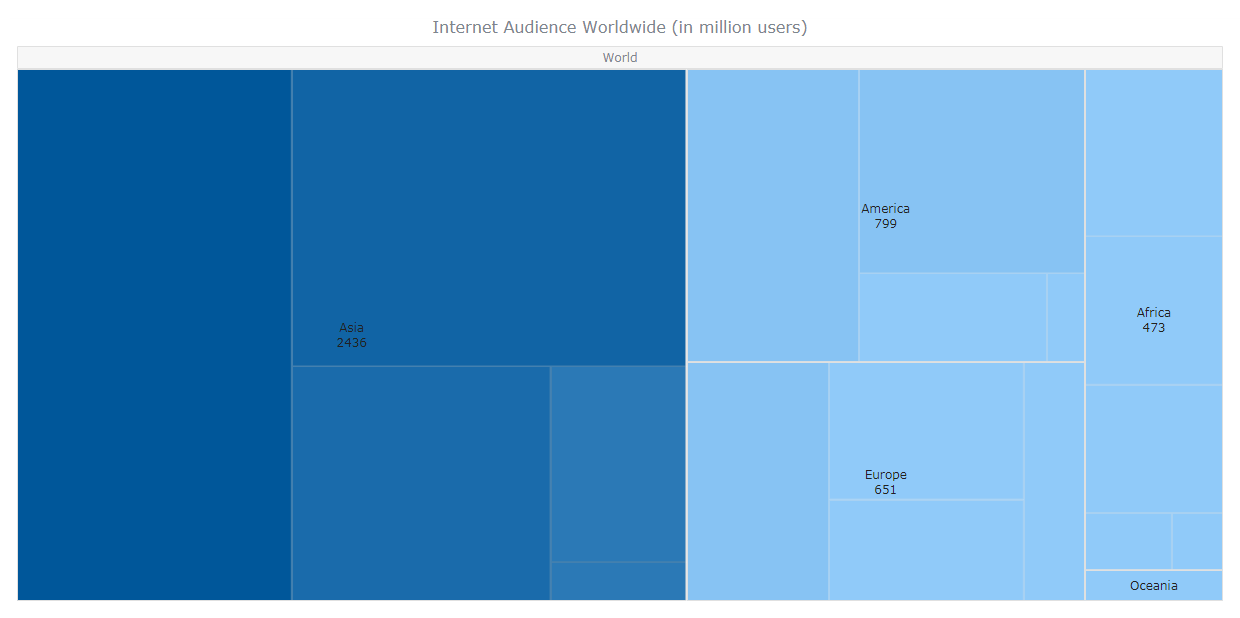
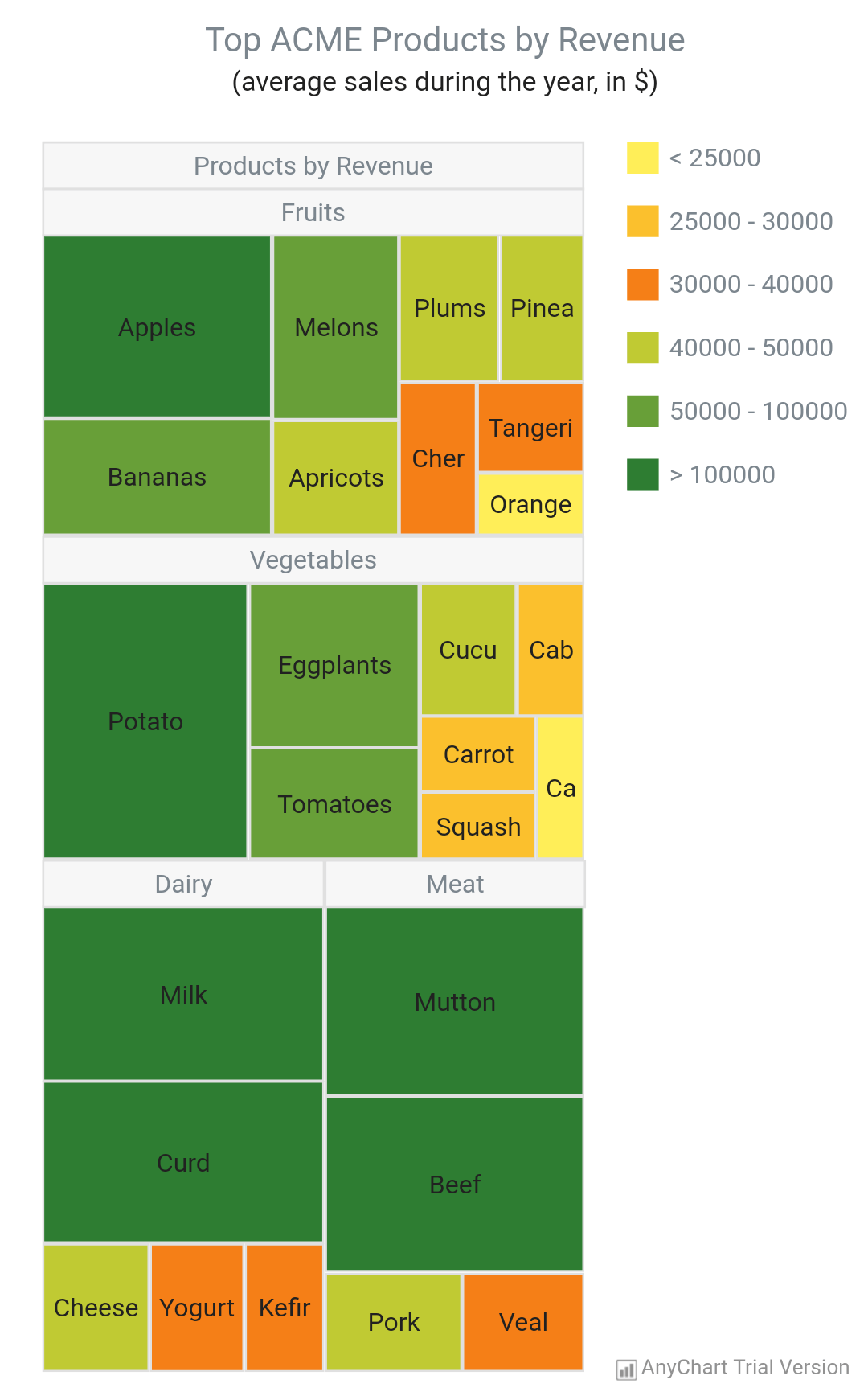
#Anychart treemap series#
Use the Series tab to set the series color and Y-Axis assignment. If the Is Logarithmic box is checked, that value will be displayed properly in the bar chart. Normally, the value 250 does not appear, due to its small value. For example, you may have the values 99999, 5002, and 250. This is useful to display data with large range differences. Select from the following options:Ĭhanges the axis to use a logarithmic scale when plotting data. Use to show or hide grid lines within the chart. Percentage (automatic on percentage type graphs). Number (does not apply for percentage type graphs).Ĭurrency (does not apply for percentage type graphs).
You can choose from the following options:
These options are available only for bubble and scatter charts. You can select each axes and set the parameters in the Axis Settings section. Based on the type of chart, displays the axes for the chart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
